Prevention of Severe Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Melalui Vaksinasi Enterovirus 71
Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55175/cdk.v51i10.1492Keywords:
Enterovirus 71, HFMD, hand, foot, and mouth disease, vaccineAbstract
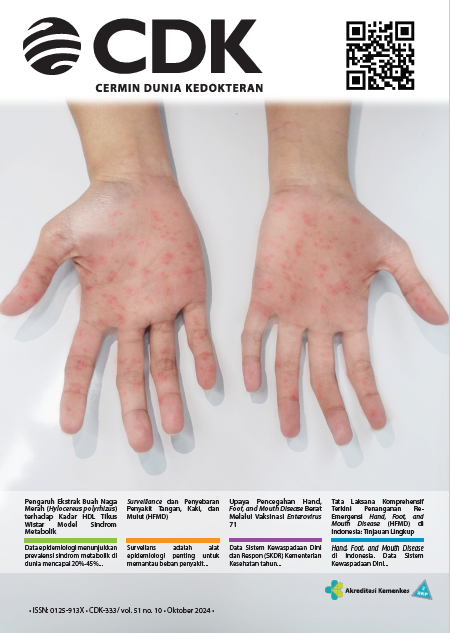
Indonesian Ministry of Health detected an increasing trend in suspected hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) in all provinces in Indonesia in 2024. Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is the main cause of severe HFMD and death. There has been no specific therapy for EV71. EV71 vaccine has been developed and approved by regulatory agencies in various countries (China, Thailand, and Indonesia) for the prevention of HFMD due to EV71. Multi-center phase IV study showed a good safety profile with an AEFI of 1,079%. Most AEFIs are grades 1 and 2.
Downloads
References
Surat Edaran Kemenkes Dirjen P2P Nomor: Sr.01.01/c/1383/2024 Tentang Kewaspadaan Terhadap Peningkatan Hand, Foot, And Mouth Disease (HFMD).
Guerra AM, Orille E, Waseem M. Hand, foot, and mouth disease [Internet]. 2024. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK431082/.
Aw-Yong KL, NikNadia NMN, Tan CW, Sam IC, Chan YF. Immune responses against enterovirus A71 infection: Implications for vaccine success. Rev Med Virol. 2019;29(5):e2073. DOI: 10.1002/rmv.2073.
Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention technical guidelines for the use of enterovirus type 71 inactivated vaccines. China CDC Immunization and Prevention; 2016. No. 74.
Cox JA, Hiscox JA, Solomon T, Ooi MH, Ng LF. Immunopathogenesis and virus–host interactions of enterovirus 71 in patients with hand, foot and mouth disease. Fronti Microbiol. 2017;8:2249. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02249.
Li ML, Shih SR, Tolbert BS, Brewer G. Enterovirus A71 vaccines. Vaccines. 2021;9:199. DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9030199.
Liu P, Yuan Y, Cui B, Huo Y, Bian L, Chen L, et al. Cross-antigenicity between EV71 sub-genotypes: Implications for vaccine efficacy. Viruses 2021;13(5):720. DOI: 10.3390/v13050720.
Ooi MH, Wong SC, Lewthwaite P, Cardosa J, Solomon T. Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of enterovirus 71. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9(11):1097-105. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70209-X.
Puenpa J, Wanlapakorn N, Vongpunsawad S, Poovorawan Y. The history of enterovirus A71 outbreaks and molecular epidemiology in the AsiaPacific region. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26(1):75. DOI: 10.1186/s12929-019-0573-2.
Putri ND, Wiyatno A, Kinobe R, Amir I, Djer MM, Adrianne A, et al. Genetic characterization of enterovirus 71 from a sibling of a fatal case of hand, foot and mouth disease in Jakarta, Indonesia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health, 2021;52:828-35.
Zhang L, Gao F, Zeng G, Yang H, Zhu T, Yang S, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of inactivated enterovirus 71 vaccine in children aged 36-71 months: A double-blind, randomized, controlled, non-inferiority phase III trial. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2021;10(4):440-7. DOI: 10.1093/jpids/piaa129.
Mao Q, Cheng T, Zhu F, Li J, Wang Y, Li Y, et al. The cross-neutralizing activity of enterovirus 71 subgenotype C4 vaccines in healthy Chinese infants and children. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(11):e79599. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0079599.
Zhu F, Xu W, Xia J, Liang Z, Liu Y, Zhang X, et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of an enterovirus 71 vaccine in China. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(9):818-28. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1304923.
Wang S, Zeng J, Zhang X, Gan Z, Fan J, Chen Y, et al. Short-term dynamic changes in neutralizing antibodies against enterovirus 71 after vaccination. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Jul 2;16(7):1595-601. DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1711678.
Hu Y, Zeng G, Chu K, Chu K, Zhang J, Han W, Zhang Y, et al. Five-year immunity persistence following immunization with inactivated enterovirus 71 type (EV71) vaccine in healthy children: A further observation. Human Vaccines Immunotherapeut. 2018;14(6):1517-23. DOI:10.1080/21645515.2018.1442997.
Zeng J, Tang T, Wang YJ, Lyu HK, Huang JH, Li X, et al., Multi center safety study of enterovirus type A71 inactivated vaccine (vero cells) after market launch, Chinese J Prev Med. 2019;53(3):252-7. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2019.03.003.
Liu X, Yang W, Zhang C, Wu H, Wang R, Ding Q, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of an inactivated enterovirus 71 vaccine co-administered with measles-mumps-rubella vaccine and live-attenuated Japanese encephalitis vaccine: A phase 4, single-center, randomized controlled trial. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021;17(12):5348-54. DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2021.2010428.
Zhang Z, Liang Z, Zeng J, Zhang J, He P, Su J, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of an inactivated enterovirus 71 vaccine administered simultaneously with hepatitis B vaccine and group A meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine: A phase 4, open-label, single-center, randomized, noninferiority trial. J Infect Dis. 2019;220(3):392-9. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiz129.
Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Health tips for hand-foot-and-mouth disease [Internet]. 2023. Available from: https://en.chinacdc.cn/health_topics/maternal_child_healthcare/202307/t20230719_267922.html.
Biovalys. Table of vaccination for children and adolescents in Thailand 2024 recommended by the pediatric infectious disease society of Thailand [Internet]. 2024. Available from: https://biovalys.com/table-of-vaccination-for-children-and-adolescents-in-thailand-2024-recommended-bythe-pediatric-infectious-disease-society-of-thailand/.
China CDC Disease Surveillance Data [Internet]. Available from: http://www.jbjc.org/article/doi/10.3784/jbjc.2021.000.
Hartoyo E. Gambaran klinis dan karakteristik genetik human enterovirus 71 penyebab hand foot and mouth disease di Banjarmasin – Kalimantan Selatan tahun 2016. Sari Pediatri 2020;21:271. DOI: 10.14238/sp21.5.2020.271-5.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Thomas Aditya

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.