Tata Laksana Komprehensif Terkini Penanganan Re-Emergensi Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) di Indonesia: Tinjauan Lingkup
Tinjauan Pustaka
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55175/cdk.v51i10.1122Kata Kunci:
Penyakit eksantema, penyakit tangan, kaki, dan mulut, ruam makulopapularAbstrak
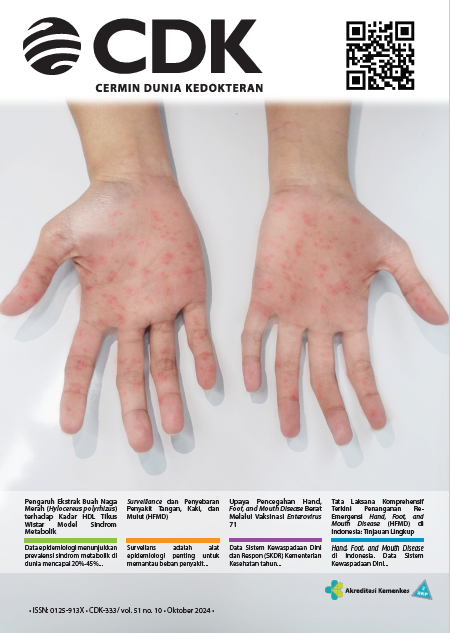
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) merupakan penyakit eksantema dengan manifestasi utama berupa erupsi ruam makulopapular pada tangan, kaki, dan mulut disertai demam dengan berbagai komplikasi berbahaya yang dapat timbul pada anak usia di bawah lima tahun. Indonesia memiliki siklus wabah HFMD berulang menjadikannya sebagai penyakit re-emergensi yang perlu diwaspadai. Penulis melakukan pencarian sistematis penelitian pada 3 database, yaitu Pubmed, Wiley Online Library, dan Science Direct, dengan kata kunci “Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease”, “enterovirus”, and “therapy” yang dipublikasikan hingga Oktober 2023. Sebanyak 791 penelitian masuk dalam analisis dan kualitasnya dinilai menggunakan Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Tata laksana komprehensif HFMD yang tersedia hingga kini mencakup upaya pencegahan, terapi, dan manajemen komplikasi. Penelitian terkini belum berhasil mengungkap pengobatan antivirus definitif, sehingga penatalaksanaan bersifat simtomatik, diikuti isolasi serta perawatan mulut dan kulit yang baik. Pada kasus berat, intervensi kasus kritis meliputi terapi antivirus, imunoglobulin intravena, serta dukungan sistem pernapasan dan sirkulasi darah. Vaksin enterovirus A71 (EV-A71) yang dinonaktifkan terbukti menjadi pilihan paling efektif dan hemat biaya untuk perlindungan jangka panjang terhadap HFMD terkait EV-A71. Namun, evolusi epidemiologi enterovirus menyebabkan intervensi yang hanya didasarkan satu agen tidak memadai, diperlukan pengembangan tata laksana definitif dan vaksin multivalen yang efektif.
Unduhan
Referensi
Ooi MH, Wong SC, Lewthwaite P, Cardosa MJ, Solomon T. Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of enterovirus 71. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9(11):1097-105. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70209-X.
Zhu P, Ji W, Li D, Li Z, Chen Y, Dai B, et al. Current status of hand-foot-and-mouth disease. J Biomed Sci. 2023;30:15. DOI: 10.1186/s12929-023-00908-4.
Nayak G, Bhuyan SK, Bhuyan R, Sahu A, Kar D, Kuanar A. Global emergence of Enterovirus 71: A systematic review. Beni Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. 2022;11(1):78. DOI: 10.1186/s43088-022-00258-4.
Guerra AM, Orille E, Waseem M. Hand, foot, and mouth disease [Internet]. 2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK431082/
Yi EJ, Shin YJ, Kim JH, Kim Tg, Chang SY. Enterovirus 71 infection and vaccines. Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2017;6(1):4–14. DOI: 10.7774%2Fcevr.2017.6.1.4.
Omana-Cepeda C, Martinez-Valverde A, del Mar Sabater-Recolons M, Jane-Salas E, Mari-Roig A, Lopez-Lopez J. A literature review and case report of hand, foot and mouth disease in an immunocompetent adult. BMC Res Notes. 2016; 9:165. DOI: 10.1186/s13104-016-1973-y.
Esposito S, Principi N. Hand, foot and mouth disease: Current knowledge on clinical manifestations, epidemiology, aetiology and prevention. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018;37(3):391–8. DOI: 10.1007/s10096-018-3206-x.
Gonzalez G, Carr MJ, Kobayashi M, Hanaoka N, Fujimoto T. Enterovirus-associated hand-foot and mouth disease and neurological complications in Japan and the rest of the world. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5201. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20205201.
Li XW, Ni X, Qian SY, Wang Q, Jiang RM, Xu WB, et al. Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease 2018 edition. World J Pediatr. 2018:14;437–47. DOI: 10.1007/s12519-018-0189-8.
Bubba L, Broberg EK, Jasir A, Simmonds P, Harvala H. Circulation of non-polio enteroviruses in 24 EU and EEA countries between 2015 and 2017: A retrospective surveillance study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(3):350–61. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30566-3.
Wang SM, Liu CC. Enterovirus 71: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2009:7(6), 735–42. DOI: 10.1586/eri.09.45.
Cheng Q, Bai L, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Wang S, Xie M, et al. Ambient temperature, humidity and hand, foot, and mouth disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ. 2018;625:828–36. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.006.
Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses [Internet]. 2013. Available from: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention. foot, and mouth disease [Internet]. 2017. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/hand-foot-mouth/index.html.
Purwanthi IGAP. Penyakit tangan, kaki, dan mulut. Cermin Dunia Kedokteran. 2016; 43(11):815-819.
Singh S, Mane SS, Kasniya G, Cartaya S, Rahman MM, Maheshwari A, et al. Enteroviral infections in infants. Newborn. 2022;1(3): 298-305. DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-11002-0036.
Ikatan Dokter Anak Indonesia. Hand, foot, and mouth disease [Internet]. 2016. Available from: https://www.idai.or.id/artikel/klinik/keluhan-anak/hand-foot-mouth-and-disease-hfmd.
He F, Rui J, Deng Z, Zhang Y, Qian K, Zhu C, et al. Surveillance, epidemiology and impact of EV-A71 vaccination on hand, foot, and mouth disease in Nanchang, China, 2010–2019. Front Microbiol. 2022;12:811553. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.811553.
Hoa-Tran TN, Dao AT H, Nguyen AT, Kataoka C, Takemura T, Pham CH, et al. Coxsackieviruses A6 and A16 associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease in Vietnam, 2008–2017: Essential information for rational vaccine design. Vaccine. 2020;38:8273–85. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.11.031.
Kang HJ, Yoon Y, Lee Y, Kim HJ, Lee DY, Lee JW, et al. A different epidemiology of enterovirus a and enterovirus b co-circulating in Korea, 2012–2019. J Pediatric. Infect Dis Soc. 2021;10:398–407. DOI: 10.1093/jpids/piaa111.
Wang X, An Z, Huo D, Jia L, Li J, Yang Y, et al. Enterovirus A71 vaccine effectiveness in preventing enterovirus A71 infection among medically-attended hand, foot, and mouth disease cases, Beijing, China. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(5):1183-1190. DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1581539.
Wang M, Chen T, Peng J, Luo Y, Du L, Lu Z, et al. The spatial-temporal distribution and etiological characteristics of hand-foot-and-mouth disease before and after EV-A71 vaccination in Kunming, China, 2017–2020. Sci Rep. 2022;12 (1):17028. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21312-2.
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Li H, Liu L. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease-associated enterovirus and the development of multivalent HFMD vaccines. Int Mol J Sci. 2023; 24(1):169. DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010169.
Abzug MJ. The enteroviruses: Problems in need of treatments. J Infect. 2014 Jan;68 Suppl 1:S108-14. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2013.09.020.
Lin JY, Kung YA, Shih SR. Antivirals and vaccines for enterovirus A71. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26(1):65. DOI: 10.1186/s12929-019-0560-7.
Oberste MS, Moore D, Anderson B, Pallansch MA, Pevear CD, Collett MS. In vitro antiviral activity of V-073 against polioviruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53(10):4501-3. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00671-09.
Collett MS, Neyts J, Modlin JF. A case for developing antiviral drugs against polio. Antiviral Res. 2008;79(3):179–187. DOI: 10.1016/j.
antiviral.2008.04.002.
Zhang HP, Wang L, Qian JH, Cai K, Chen YH, Zhang QL, et al. Efficacy and safety of ribavirin aerosol in children with hand-foot-mouth disease. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014;16(3):272-6.
Huang X, Zhang X, Wang F, Wei H, Ma H, Sui M, et al. Clinical efficacy of therapy with recombinant human interferon alpha1b in hand, foot, and mouth disease with enterovirus 71 infection. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(2): e0148907. DOI: 10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0148907.
Lin H, Huang L, Zhou J, Lin K, Wang H, Xue X, et al. Efficacy and safety of interferon-alpha2b spray in the treatment of hand, foot, and mouth disease: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial. Adv Virol. 2016;161(11):3073–80.
Wang SM, Liu CC. Enterovirus 71: Epidemiology, pathogenesis and management. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2009;7(6):735–42.
Wang SM. Milrinone in enterovirus 71 brain stem encephalitis. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:82. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00082.
Wang C, Cui Y, Zhu Y, Wang F, Rong Q, Zhang Y. Continuous hemodiafiltration as a rescue therapy for patients with cardiopulmonary failure caused by enterovirus-71: A retrospective observational study in a PICU. BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Oct 21;19(1):866. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-4519-9.
Hsia SH, Lin JJ, Chan OW, Lin TY. Cardiopulmonary failure in children infected with enterovirus A71. J Biomed Sci. 2020 Apr 16;27(1):53. DOI: 10.1186/s12929-020-00650-1.
Yang TT, Huang LM, Lu CY, Kao CL, Lee WT, Lee PI, et al. Clinical features and factors of unfavorable outcomes for non-polio enterovirus infection of the central nervous system in northern Taiwan, 1994–2003. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2005;38(6):417–24.
Cai K, Wang Y, Guo Z, Yu H, Li H, Zhang L, Lin TY. Clinical characteristics and managements of severe hand, foot and mouth disease caused by enterovirus A71 and coxsackievirus A16 in Shanghai, China. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19(1):285. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-3878-6.
Jiao W, Tan SR, Huang YF, Mu LH, Yang Y, Wang Y, et al. The effectiveness of different doses of intravenous immunoglobulin on severe hand, foot and mouth disease: A meta-analysis. Med Princ Pract. 2019 Jun;28(3):256–63. DOI: 10.1159/000496926.
Yan Z, Shang Y, Li F, Xie F, Qian H, Zhang Y, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of phentolamine in the management of severe hand, foot and mouth disease combined with pulmonary edema. Exp Ther Med. 2017 Apr;13(4):1403-7. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4104.
Li Xh, Li Sj, Xu Y, Wei D, Shi QS, Zhu QX, et al. Effect of integrated chinese and western medicine therapy on severe hand, foot and mouth disease: A prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Chin J Integr Med. 2017;23:887–92. DOI: 10.1007/s11655-016-2504-3.
Li X, Zhang C, Shi Q, Yang T, Zhu Q, Tian Y, et al. Improving the efficacy of conventional therapy by adding andrographolide sulfonate in the treatment of severe hand, foot, and mouth disease: A randomized controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:316250. DOI: 10.1155/2013/316250.
Lin H, Zhou J, Lin K, Wang H, Liang Z, Ren X, et al. Efficacy of Scutellaria baicalensis for the treatment of hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with encephalitis in patients infected with EV71: A multicenter, retrospective analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2016:5697571. DOI: 10.1155/2016/5697571.
Unduhan
Diterbitkan
Cara Mengutip
Terbitan
Bagian
Lisensi
Hak Cipta (c) 2024 Muhammad Alifian Remifta Putra

Artikel ini berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.