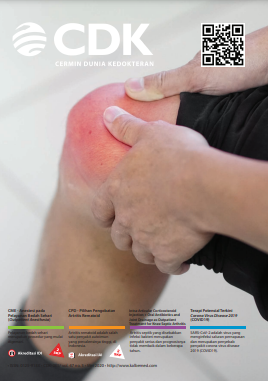
Intra-Articular Corticosteroid Injection + Oral Antibiotics and Joint Drainage as Outpatient Treatment for Knee Septic Arthritis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55175/cdk.v47i4.366Keywords:
Outpatient care, septic arthritisAbstract
Septic arthritis caused by bacterial infection is a serious disease and the prognosis has not improved significantly over the past two decades. The most often etiology is Staphylococcus aureus. The diagnosis of septic arthritis rests on isolation of the pathogen from joint fluid. Appropriate antibiotic treatment and adequate joint drainage should begin immediately in suspected septic arthritis after collection of proper sample for microbiologic studies. This case was treated with intra-articular triamcinolon acetonide injection, oral amoxicilin-clavulanate, and needle aspiration for joint drainage.
Artritis septik yang disebabkan infeksi bakteri merupakan penyakit serius dan prognosisnya tidak membaik dalam beberapa tahun. Etiologi tersering artritis septik adalah Staphyloccocus aureus. Diagnosis artritis septik harus berdasarkan isolasi bakteri patogen dari cairan sendi. Pemberian antibiotik dan drainase cairan sendi harus segera jika dicurigai artritis septik setelah sediaan mikrobiologi diambil. Kasus ini menggunakan injeksi kortikosteroid triamcinolon acetonide ke dalam sendi lutut bersamaan dengan antibiotik oral amoksilin-klavulanat dan aspirasi cairan sendi untuk drainase.
Downloads
References
William WCS, Driver CB. Septic arthritis (infectious arthritis) [Internet]. 2018 Mar [cited 2018 Sept 5]. Available from: https://www.medicinenet.com/septic_arthritis/article.htm#which_health_care_professionals_specialize_in_the_diagnosis_and_treatment_of_septic_arthritis
Von Essen R, Savolainen HA. Bacterial infection following intra-articular injection – a brief review. Scand J Rheumatol 1989;18:7-12.
Hughes LB. Infectious arthritis. In: Koopman WJ, Moreland LW. eds. Arthritis and allied conditions. A textbook of rheumatology. 15th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins 2005 .p. 2577-601.
Shirtliff ME, Mader J. Acute septic arthritis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002;15(14):527-44
Gupta MN, Sturrock RD, Field M. A prospective 2-year study of 75 patients with adult-onset septic arthritis. J Rheumatol 2001;40:24-30.
Farrow L. A systematic review and meta-analysis regarding the use of corticosteroids in septic arthritis. BMC Musculoskeletal Disord 2015;16:241
Buttgereit F, Burmester GR, Straub RH, Seibel MJ, Zhou H. Exogenous and endogenous glucocorticoids in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:1–9.
Backstein D, Hutchison C, Gross A. Septic arthritis of the hip after percutaneous femoral artery catheterization . J Arthroplasty 2002;17(8):1074-7.
Klein RS. Joint infection, with consideration of underlying disease and sources of bacteremia in hematogenous infection. Clin Geriatr Med. 1988;4(2):375-94.
Morgan DS, Fisher D, Merianos A,Currie BJ. An 18 year clinical review of septic arthritis from tropical Australia. Epidemiol Infect. 1996;117(3):423-8.
Brusch JL. Septic arthritis [Internet]. 2018. Available from: http://www.emedicine. com/med/topic3394.htm.
Siva C, Velazquez C, Mody A, Brasington R. Diagnosing acute monoarthritis in adults: A practical approach for the family physician. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(1):83-90.
Zuber TJ. Knee joint aspiration and injection. Am Fam Physician. 2002;66(8):1497-500, 1503-4, 1507.
Sibbit WL Jr, Kettwich LG, Band PA, Chavez-Chiang NR, DeLea SL, Haseler LJ, et al. Does ultrasound guidance improve the outcomes of arthrocentesis and corticosteroid injection of the knee? Scand J Rheumatol. 2012;41(1):66-72.
Zhang Q, Zhang T, Lv H, Xie L, Wu W, Wu J, Wu X. Comparison of two positions of knee arthrocentesis: how to obtain complete drainage. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;91(7):611-5.
Shlamovitz GZ, Schraga ED. Knee arthrocentesis. Medscape [Internet]. 2018. Available from: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/79994-overview
Luukkainen R, Nissila M, Asikainen E, Sanila M, Lehtinen K, Alanaatu A, et al. Periarticular corticosteroid treatment of the sacroiliac joint in patients with seronegative spondyloarthropathy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1999;17:88–90.
Wang JJ, Ho ST, Lee SC, Tang JJ, Liaw WJ. Intraarticular triamcinolone acetonide for pain control after arthroscopic knee surgery. Anesth Analg. 1998;87:113–6.
Wysenbeek AJ, Volchek J, AmitM, Robinson D, Boldur I, Nevo Z. Treatment of staphylococcal septic arthritis in rabbits by systemic antibiotics and intra-articular corticosteroids. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998;57:687–90.
Saez-Llorens X, Mustafa M, Ramilo O, Fink C, Beulter B, Nelson JD. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 B in synovial fluid of infants and children with suppurative arthritis. Am J Dis Children 1990;144:353–6.
Gray RG, Tenenbaum J, Gottlieb NL. Local corticosteroid injection therapy in rheumatic disorders. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1981;10:231–54.
Kaandrop CJ, van Schaardenburg D, Krijnen P. Antibiotic prophylaxis of haematogenous bacterial arthritis. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1999;143:1808–11
Fitzgerald RH Jr. Intrasynovial injection of steroids: uses and abuses. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976;51:655–9.
Hultgren O, Kopf M, Tarkowski A. Staphylococcus aureus-induced septic arthritis and septic: Death is decreased in IL-4-deficient mice: Role of IL-4 as promoter for bacterial growth. J Immunol. 1998; 160:5082-7.
Shetty AK, Gedalia A. Septic arthritis in children. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1998;24(2):287-304.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Cermin Dunia Kedokteran

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.